What is Teleradiology?
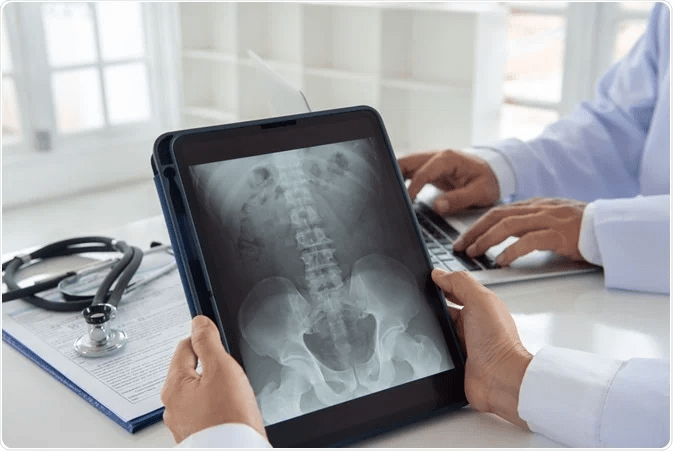
Telemedicine uses various technologies to transfer clinical information, and the internet has expanded its reach across all medical specialties. One significant application in radiology is called “teleradiology.”
Radiology involves medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose or treat patients. Teleradiology allows these images to be obtained, viewed, and interpreted remotely by radiologists for diagnostic or consultation purposes.
As a relatively new practice, teleradiology is increasingly being adopted by hospitals, urgent care centers, and imaging specialists. This growth is largely due to its ability to address shortages in radiological staff and expertise.
The teleradiology process relies on three essential components: an image-sending station, a transmission network, and a receiving station equipped with a high-quality display approved for clinical use. Today, specialized software enables radiological images to be shared as easily as email attachments.
Advantages of Teleradiology
Teleradiology improves patient care by giving radiologists the ability to provide expertise remotely. This is especially valuable when specialists like MRI, pediatric, or neuro-radiologists are needed, as they often work in large urban centers and may not be available to patients in remote locations outside regular business hours.
Smaller or rural hospitals often lack sufficient radiological coverage, sometimes relying on a single radiologist or none at all. In cases where local radiologists lack specialized training, teleradiology allows them to consult with expert radiologists to ensure accurate diagnoses.
Additionally, teleradiology enables collaboration between healthcare professionals across great distances, helping to obtain second opinions from specialists. Hospitals can also partner with outsourcing companies or radiology groups, allowing them to make the most of their own staff while maintaining regular working hours and providing uninterrupted care.
Teleradiology can be cost-effective, as hospitals only pay for each radiological exam performed by the outsourced provider. This system helps smaller hospitals offer high-quality care without the need for full-time radiology specialists on-site.
Challenges of Teleradiology
While teleradiology has many benefits, it also presents challenges. Outsourcing radiological services may impact the role and perception of in-house radiologists, potentially making them feel less valued. In extreme cases, their jobs could be threatened if their work is seen as replaceable by external providers.
Additionally, teleradiology limits a radiologist’s ability to directly follow up with patient procedures, potentially leading to communication gaps with on-site doctors. Clear and effective communication is essential to avoid misinterpretations.
Finally, teleradiology is entirely dependent on technology. Without reliable internet access, teleradiology becomes unavailable, leaving patients undiagnosed or untreated until service is restored.
